Topics
Phylogeny and cumulative transmission of SARS-CoV-2 with S protein D614G mutation in Europe
The viral S protein interacts with ACE2 surface proteins on target cells and mediates viral entry into the cell. The Phylogenetic analysis reveals an early branching event in SARS-CoV-2 evolution. The S D614G mutation is dominant in the early European infection clusters. Sequence analysis suggests further transmission of this strain to North America and subsequent reintroduction events from the USA to many European countries. Most of the patient samples from Austrian patients show the same S D614G mutation shared by many other European strains. It is not clear whether this S D614G mutation has an effect on the function of the S protein.
Phylogenetische und kumulative Übertragung von SARS-CoV-2 mit S Protein D614G Mutation
Das virale S Protein interagiert mit dem ACE2 Protein auf Zielzellen und verschafft dem Virus auf diese Weise Zutritt in diese. Die phylogenetische Analyse offenbart eine frühe Verzweigung in der SARS-CoV-2 Evolution. Die S D614G Mutation ist dabei dominierend in den frühen europäischen Infektions-Clustern. Eine Analyse der Sequenzen zeichnet weitere Übertragungen dieses Stamms nach Nord-Amerika nach, darüberhinaus direkt anschließend eine Wiedereinführung dessen von den USA zu vielen anderen europäischen Ländern. Die meisten österreichischen Patienten-Proben zeigen dieselbe S D614G Mutation, die in vielen anderen europäischen Stämmen ebenfalls zu finden ist. Es ist noch unklar, ob diese S D614G Mutation einen Effekt auf die Funktionsweise des S Proteins hat.
The illustration was generated by data-driven vector-graphics extracted from Nextstrain.org, enabled by data from GISAID.org, world map-data from Openstreetmap.org and 3D elements rendered with Octane renderer for Unity3D.
Diese Abbildung wurde generiert mit Daten-unterstützten Vektorgraphiken extrahiert von Nextstrain.org, unterstützt durch Daten von GISAID.org, Openstreetmap.org und 3D Elementen mit Octane Renderer für Unity3D.
© Bobby Rajesh Malhotra / CeMM (Creative Commons license: CC BY-NC)
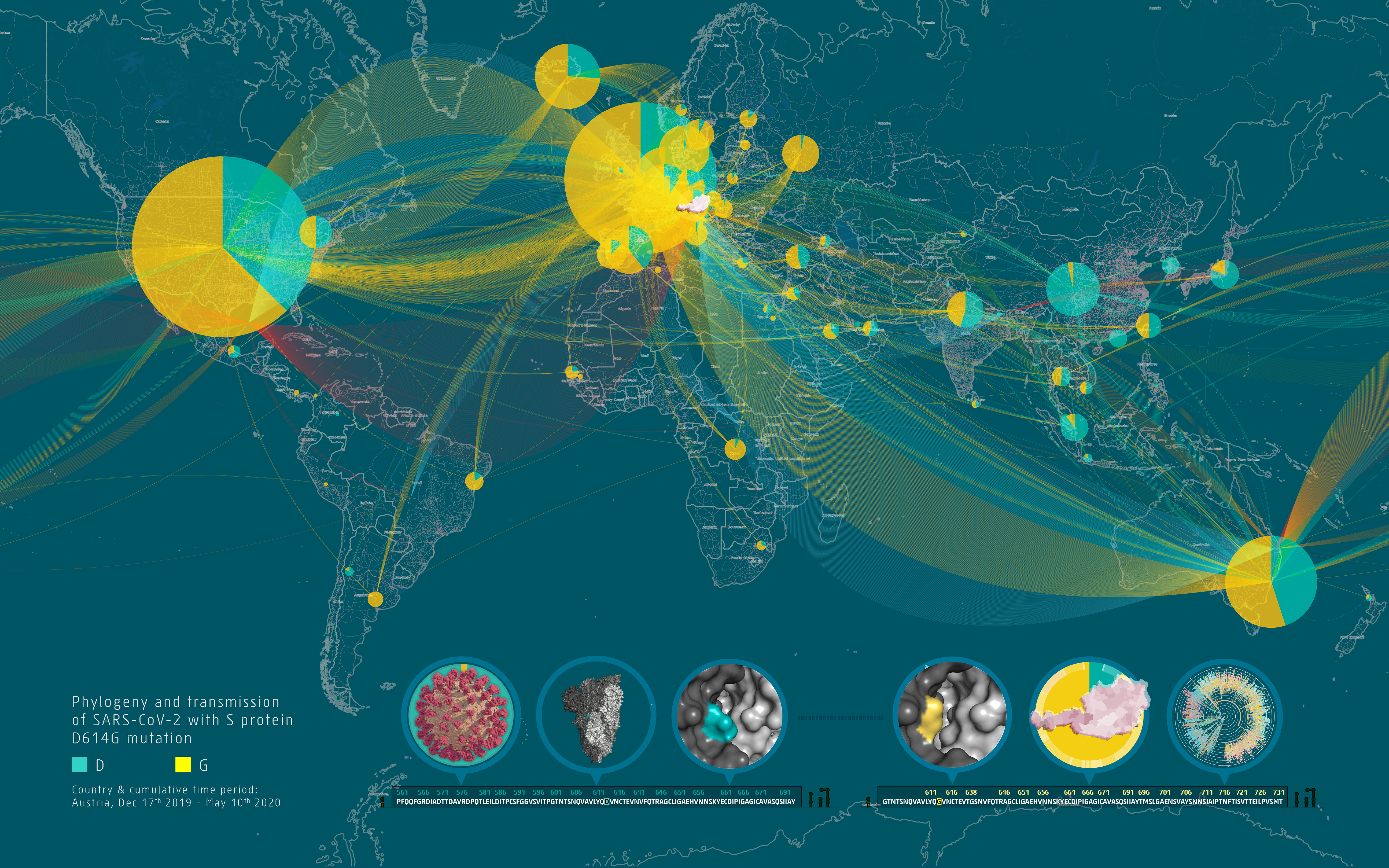
Global SARS-CoV-2 transmission and emergence of the S protein D614G mutation
The D614G mutation in the viral S protein represents an early branching point that is dominant in the European infection clusters and parts of North America. Sequence analysis suggests further transmission of this strain to North America and subsequent reintroduction events from the USA to many European countries. Most of the Austrian patient samples show the same S D614G mutation shared by many other European strains.
Die D614G Mutation im viralen S Protein repräsentiert eine frühe Gabelung der Transmissionskette in Europa. Sequenzanalysen deuten darauf hin, dass eine Transmission dieses Virus nach Nordamerika und wieder zurück in viele europäische Länder stattgefunden hat. Die Mehrzahl der sequenzierten Virusgenome aus Österreich enthält diese D614G Mutation.
The illustration was generated by data-driven vector-graphics extracted from Nextstrain.org, enabled by data from GISAID.org, world map-data from Openstreetmap.org and 3D elements rendered with Octane renderer for Unity3D.
Diese Abbildung wurde generiert mit Daten-unterstützten Vektorgraphiken extrahiert von Nextstrain.org, unterstützt durch Daten von GISAID.org, Openstreetmap.org und 3D Elementen mit Octane Renderer für Unity3D.
© Bobby Rajesh Malhotra / CeMM (Creative Commons license: CC BY-NC)
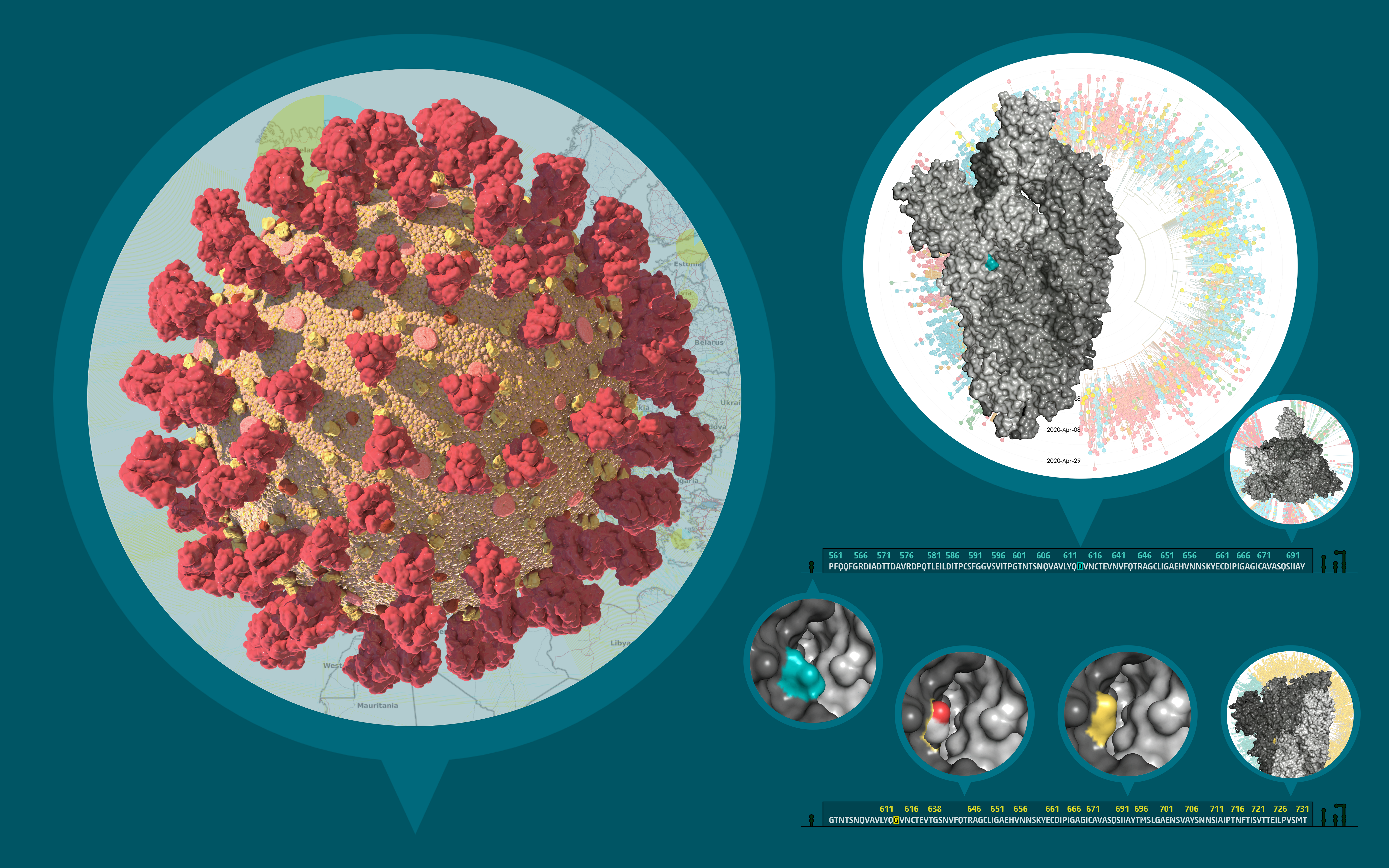
SARS-CoV-2 virion, phylogeny and structural effects of the D614G mutation in the S protein
To the left, this composite image depicts the three-dimensional structure of SARS-CoV-2 virion based on custom mesoscale 3D-model of SARS-CoV-2 with RCSB PDB 3D-surface data and experimental protein structures (PDB: 6VSB, 6VXX, 6VXY). To the top right, the three-dimensional structure of the viral S protein and a phylogenetic tree of international SARS-CoV-2 genomes is shown. To the bottom right, the predicted conformational change in the S protein structure caused by the D614G mutation is shown.
Diese zusammengesetzte Abbildung zeigt auf der linken Seite die dreidimensionale Struktur eines SARS-CoV-2 Virions basierend auf einem 3D Model mit experimentell bestimmten Proteinstrukturen (PDB: 6VSB, 6VXX, 6VXY). Auf der rechten Seite ist die dreidimensionale Struktur des viralen S Proteins dargestellt, sowie ein phylogenetischer Stammbaum der internationalen SARS-CoV-2 Genome (Nextstrain.org, GISAID.org). Darunter sind die vorausberechneten Änderungen in der S Protein Struktur dargestellt, die durch die D614G Mutation hervorgerufen werden.
The illustration was generated by data-driven vector-graphics extracted from Nextstrain.org, enabled by data from GISAID.org, world map-data from Openstreetmap.org and 3D elements rendered with Octane renderer for Unity3D.
Diese Abbildung wurde generiert mit Daten-unterstützten Vektorgraphiken extrahiert von Nextstrain.org, unterstützt durch Daten von GISAID.org, Openstreetmap.org und 3D Elementen mit Octane Renderer für Unity3D.
© Bobby Rajesh Malhotra / CeMM (Creative Commons license: CC BY-NC)
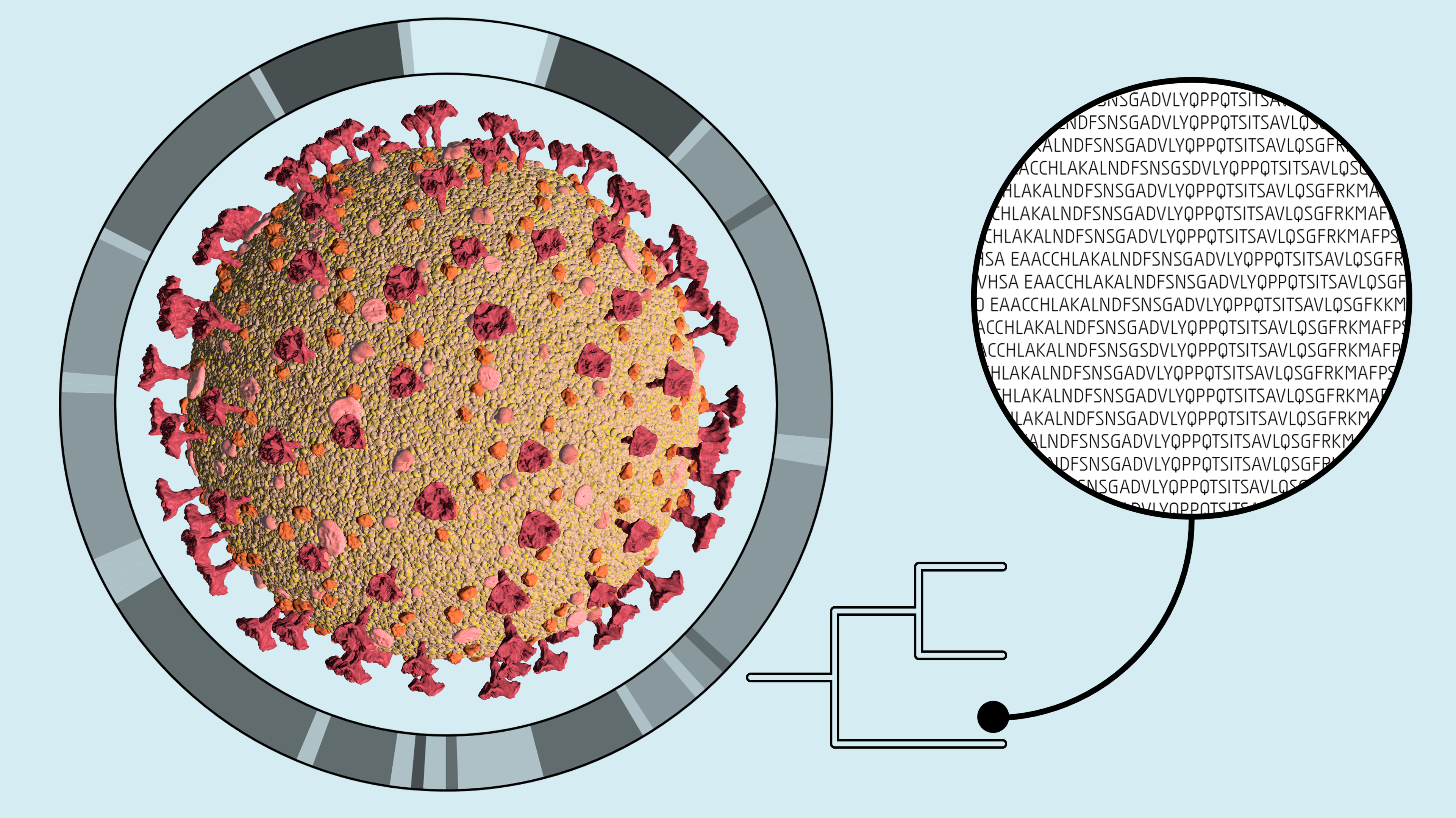
SARS CoV-2 Sequencing
Illustration created in Unity3D & Octane Renderer for Unity.
Illustration mit Unity3D & Octane Renderer für Unity erstellt.
© Bobby Rajesh Malhotra / CeMM
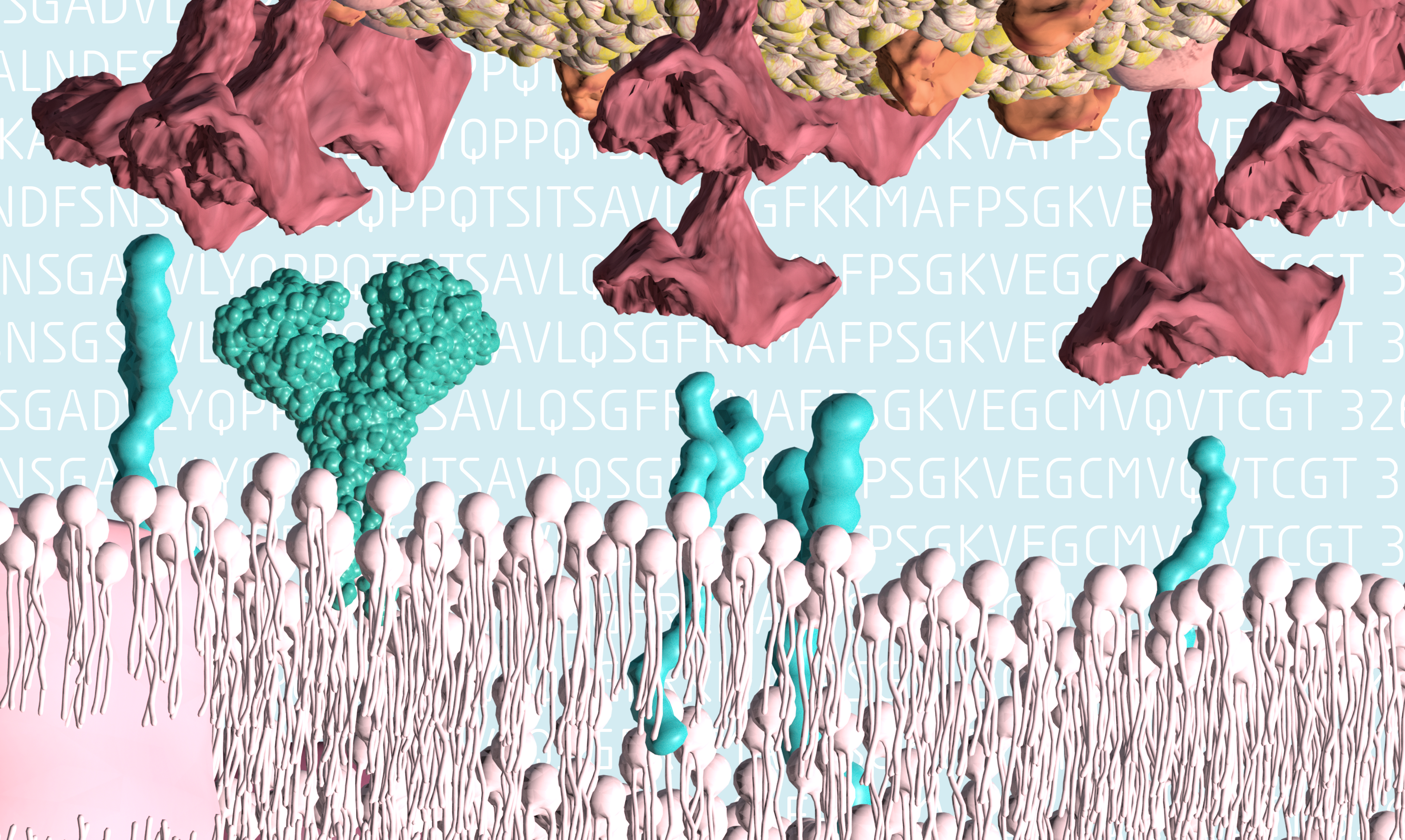
SARS CoV-2 docking ACE2 receptor
SARS CoV-2 docking the ACE2 receptor in human cells.
SARS CoV-2 bindet an den ACE2-Rezeptor auf menschlichen Zellen.
Illustration created in Unity3D & Octane Renderer for Unity.
Illustration mit Unity3D & Octane Renderer für Unity erstellt.
© Bobby Rajesh Malhotra / CeMM

